THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
DISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT BY A GLASS
PRISM
When sunlight passes through a small hole, it gives a narrow beam of white light.
Allow the light beam to fall on the face of a glass prism.
The prism splits the incident
white light into a band of 7 colours. They are Violet, Indigo, Blue,
Green, Yellow, Orange and Red (VIBGYOR).
The band of the coloured
components of a light beam is called its spectrum.
The splitting of light into its
component colours is called dispersion.
Different colours of light bend in
different angles with respect to the incident ray. The red light bends the
least while the violet the most. Thus the rays of each colour emerge
along different paths and become distinct.
Isaac Newton
was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the solar spectrum. He tried to
split the colours of the spectrum of white light further by using another
similar prism. However, he did not get any more colours. He then placed a
second identical prism in an inverted position with respect to the first prism.
The colours of the spectrum passed through the second prism and emerged as a
beam of white light from the other side of second prism. Thus Newton proposed the
idea that the sunlight is made up of 7 colours.
Any light that gives a spectrum
similar to that of sunlight is referred to as white light.
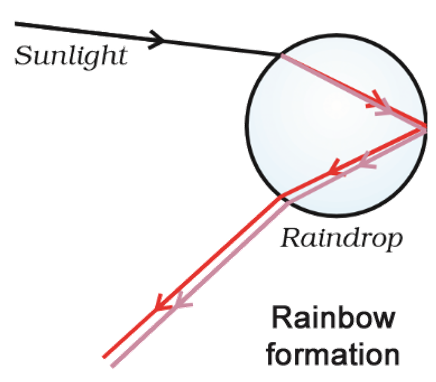
A rainbow is a natural spectrum. It is always
formed in a direction opposite to the Sun. The rain water droplets in
the atmosphere act like small prisms. They refract and disperse
the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally. It again refracts
when comes out of the raindrop. Due to dispersion and internal
reflection, different colours reach the observer’s eye.
Rainbow can be also seen when look
at the sky through a waterfall, with the Sun behind us.