CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS
TYPES OF
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
1. Combination Reactions
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
+ Heat
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime)
Formation of slaked lime
Slaked lime solution
is used for whitewashing. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with CO2
in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) after 2-3
days of whitewashing giving a shiny finish to the walls. Marble is also CaCO3.
Other examples of combination reactions:
(i) Burning of coal:
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
(ii) Formation of water from H2
and O2:
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
Reactions in which heat is released
along with formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions.
Other examples of exothermic
reactions:
(i)
Burning of natural gas:
CH4(g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2
(g) + 2H2O (g)
(ii) Respiration:
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(aq) → 6CO2(aq) + 6H2O(l) + energy
(Glucose)
(iii)
Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost.
(iv) Burning magnesium to form
magnesium oxide.
2. Decomposition Reactions
These are the reactions in
which single reactant breaks down to give simpler products.
Examples:
- Take 2 g ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube. Heat it over flame. Green colour of ferrous sulphate is changed with characteristic odour of burning sulphur. When heated, ferrous sulphate (FeSO4. 7H2O) lose water. It then decomposes to ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3).
- Decomposition of CaCO3 to calcium oxide (CaO) & CO2 on heating is used in industries. CaO has many uses (e.g. manufacture of cement). When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, it is called thermal decomposition.
2AgCl (s)
Silver bromide also behaves in
the same way.
2AgBr (s)
Ba(OH)2 +NH4Cl
→ BaCl2 + NH4OH
3. Displacement Reactions
Examples:
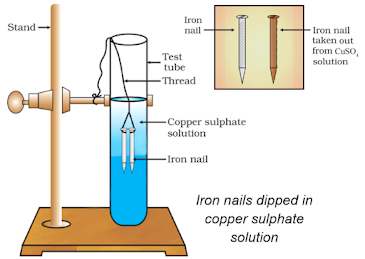
Take 3 iron nails cleaned by rubbing with sand paper.
Take two test tubes A and B. Add 10 mL copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution in each test tube.
Immerse two iron nails in CuSO4 in test tube B. Keep one iron nail aside for comparison.
After 20 minutes, take out the iron nails. They become brownish in colour. Blue colour of CuSO4 solution fades.
This is due to the following chemical reaction:
Other examples of displacement reactions:
Zinc and lead are more reactive elements than copper. They displace copper from its compounds.
These are the reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactants.
Examples:
Take 3 mL sodium sulphate solution in a test tube. In another test tube, take 3 mL barium chloride solution. Mix the two solutions.
A white substance (BaSO4) is formed by the reaction of SO42– and Ba2+. This water insoluble substance is called precipitate. Any reaction that produces a precipitate is called precipitation reaction.
The other product (sodium chloride) remains in solution.
Reaction between lead nitrate & potassium
iodide to form a yellow precipitate of lead iodide.
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ 2KI(aq) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
5. Oxidation and
Reduction
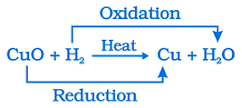
2Cu + O2
If hydrogen gas is passed over the heated CuO, the black coating turns brown as the reverse reaction takes place and copper is obtained.
CuO + H2
Other examples of redox
reactions:
Carbon is
oxidised to CO and ZnO is reduced to Zn.
ZnO + C → + Zn +
CO
HCl is oxidised
to Cl2 whereas MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2.
MnO2
+ 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
If a substance gains oxygen
or loses hydrogen during a reaction, it is oxidised. If a substance loses
oxygen or gains hydrogen during a reaction, it is reduced.
A magnesium
ribbon burns in air (oxygen) to form magnesium oxide. Here magnesium is
oxidised.
EFFECTS OF
OXIDATION REACTIONS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1. Corrosion
2. Rancidity
- Adding antioxidants (substances which prevent oxidation) to foods containing fats and oil.
- Keeping food in air tight containers.
- Flushing bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen.