LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
1. Name the portion of the myofibril between
two successive Z-lines. (Score 1)
(a) H-zone
(b) Sarcomere
(c) I-band
(d) M-line
Answer:
(b) Sarcomere
a) Identify figures A and B.
b) Name the subunits of A and B. (Score 2)
Answer:
(a) A= Actin, B= Myosin.
(b)
A= G- actin, B= Meromyosin (HMM + LMM)
Answer:
Cross bridge formation during muscle contraction.
A= Actin filament. B= Myosin filament. C= Cross bridge.
Answer:
Ca ion binds with a
subunit of troponin on actin filaments and unmask the active sites for myosin.
Using energy from ATP
hydrolysis, myosin head binds to active sites on the actin to form cross
bridge.
5. Compete
the following chart showing the structure of myosin filament and its protein based
on the hints given in the brackets. (Score 2)
(Light meromyosin, Actin, Tropomyosin, Meromyosin)
Answer:
(A) Meromyosin
(B) Light meromyosin
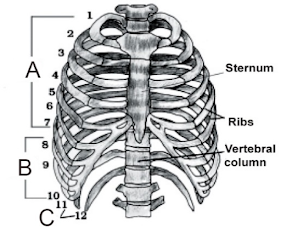
(b) First 7 ribs are ventrally
connected to sternum with the help of …………….
Answer:
(a) A= True ribs, B= False ribs, C= Floating ribs.
(b) Hyaline cartilage.
Answer:
a. Fibrous (immovable) joints: E.g. sutures b/w skull bones.
b. Cartilaginous joints (Slightly movable
joints): E.g. Joints between the adjacent
vertebrae.
c. Synovial (movable) joints: E.g. Shoulder joint.
a.
Inflammation of joints.
b.
Decreased bone mass and increased chance
of fracture.
c.
Inflammation of joints due to the
accumulation of uric acid crystals.
d.
Rapid spasms in muscles due to low Ca++
in body fluids.
Answer:
(a) Arthritis
(b) Osteoporosis
(c) Gout
(d) Tetany