4. MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
2020
SAY
1. Find out the
initiator codon among the following: (1)
(a)
ACG (b) AUC
(c)
AUG (d) AAG
ü Answer:
(c) AUG
2. (a) Complete
the flow chart given below showing DNA finger-printing technique.
(b) Who developed the DNA finger-printing technique?
(c) Write the full form of VNTR. (2)
ü Answer:
(a) (i) Digestion of DNA by restriction endonuclease.
(ii)
Hybridisation using labelled VNTR probe.
(b) Alec Jeffreys
(c) Variable Number of Tandem Repeats.
3. Schematic
structure of a transcription unit is given below: (2)
(a)
Identify a, b
and c.
(b) The coding sequences/expressed sequences in eukaryotes are known as ...................
ü Answer:
(a) a. Promoter. b. Structural genes. c. Terminator.
(b) Exons
4. Lactose
catabolism in the absence of inducer in E. Coli is given below: (3)
(a)
Identify ‘P’.
(b)
Draw the
diagram in the presence of inducer.
(c)
Write the enzymes
produced by the structural genes ‘z’, ‘y’ and ‘a’.
ü Answer:
(a) Promoter.
(b)
(c) z: b-galactosidase, y: Permease, a: Transacetylase.
2020
MARCH
1. One of the
salient features of genetic code is "Universal". (2)
a.
Write any other
two salient features of genetic code.
b.
Which is the initiator
codon? And name the amino acid it codes.
ü Answer:
(a) Genetic code is degenerate.
Genetic code is unambiguous.
(b) Initiator codon: AUG
Name of amino acid it codes: Methionine.
2. Observe the figure
given below: (3)
a. Identify the
process in the picture.
b. Name any two
enzymes needed for this process.
c. Write the
peculiarities of the newly synthesized daughter strands.
ü Answer:
(a) DNA replication.
(b) DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, Helicase etc.
(c) One strand is formed as continuous strand
(leading strand). Other strand is formed as small stretches (Okazaki
fragments).
3. A DNA sequence
is provided below. (3)
5' - ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCAT - 3'
a. Write down the
sequence of its complementary strand.
b. Name the enzyme
involved in transcription of DNA.
c. What would
happen if both the strands of the DNA act as templates for transcription?
ü Answer:
(a) 3' – TACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTA – 5’
(b) DNA dependent RNA polymerase.
(c) It results in the production of 2 RNA molecules
simultaneously. This would be complimentary to each other. It forms a double
stranded RNA and prevents translation.
2019
SAY June
1. In a double
stranded DNA, the ratios between Adenine and Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine are
constant and equal one. Who observed this fact? (1)
ü Answer:
Erwin Chargaff
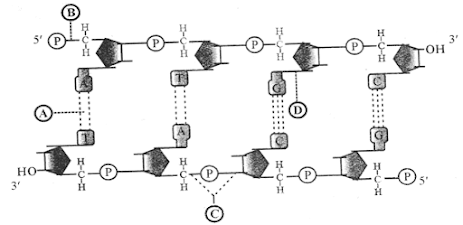
2. Observe the
diagram of a double stranded DNA strand: (2)
Identify the bonds A, B, C & D.
ü Answer:
A= Hydrogen bond
B= Ester bond
C= Phosphodiester bond
D= N-glycosidic bond
3. The following
diagram shows a process in the Ribosome: (2)
Identify the process and explain.
ü Answer:
The process is Translation (Protein synthesis).
It includes 4 steps:
a.
Charging
(aminoacylation) of tRNA.
b.
Initiation.
c.
Elongation.
d.
Termination.
4. Transcription
of eukaryotes are more complicated than that of prokaryotes. Explain any two
additional complexities found in the transcription of eukaryotes. (3)
ü Answer:
· There are 3 RNA polymerases: RNA polymerase I, II
& III.
· Primary transcripts (hnRNA) contain exons &
introns. To remove intro ns, it undergoes processing (splicing, capping &
tailing) and becomes mRNA.
2019
MARCH
1. Diagrammatic
representation of the central dogma given below is not correct. Make necessary
corrections and redraw it. (1)
ü Answer:
2. Observe the
figure given below: (2)
a.
Identify the
figure.
b.
How many
histone molecules are present in the Histone core.
c.
Distinguish
Euchromatin and Heterochromatin.
ü Answer:
(a) Nucleosome.
(b) 8
(c) Euchromatin: Loosely packed, light stained
and transcriptionally active region of chromatin.
Heterochromatin: Densely packed, dark stained and inactive region of
chromatin.
3. Diagrammatic representation
of the DNA fingerprint from a crime scene and that of a suspected person are
given below: (3)
a.
What is your
conclusion about the suspects based on DNA Fingerprint given?
b.
What is VNTR?
c.
Who developed
this technique first?
ü Answer:
a.
Suspect
II may be responsible for the crime. Because DNA from crime scene matches with
DNA of suspect II.
b.
A
DNA sequence which is tandemly repeated in many copy numbers is called variable
number tandem repeats (VNTR).
c.
Alec
Jeffreys.
4. The diagrammatic
representation of a process in bacteria is given below: (3)
a.
Identify the
process.
b.
Name the enzyme
involved in this process.
c.
Explain the
three major steps in this process.
ü Answer:
a.
Transcription
(RNA synthesis)
b.
RNA
polymerase.
c.
Initiation: RNA polymerase binds at the promoter site of
DNA.
Elongation: RNA chain is synthesized in 5’-3’ direction.
Termination: A termination factor (ρ factor) binds to the RNA
polymerase and terminates the transcription.
2018
SAY
1. 'Human genome
project is a mega project" Give two reasons to explain this. (2)
ü Answer:
It was a 13-year long project.
It has sequenced 3 x 109 bp in human
genome with the help of computer.
It has identified about 30,000 genes in human genome.
2. Observe the
diagram and answer the following questions: (2)
a.
Identify the
diagram.
b.
Name the
enzymes A, B and C.
ü Answer:
(a) Lac operon.
(b) A= beta galactosidase, B= Permease,
C= Transacetylase.
3. "Genetic
code is universal in nature"
a.
Substantiate
this statement.
b.
Mention any two
other salient features of genetic code. (2)
ü Answer:
(a) It means from bacteria to human, each triplet
codon codes for the same amino acid.
(b) Genetic code is unambiguous.
Genetic code is degenerate.
4. Expand the
following: (3)
a.
SNP
b.
BAC
c.
YAC
ü Answer:
(a) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
(b) Bacterial Artificial Chromosome
(c) Yeast Artificial Chromosome.
2018
MARCH
1. Expressed
sequences in the gene are called (1)
(a) Introns (b)
Mutons
(c) Exons (d) Cistrons
ü Answer:
(c)
Exons
2. DNA is tightly
packed structure and is found as units called nucleosomes. (2)
(a) Explain the concept of nucleosomes.
(b) Differentiate between euchromatin & heterochromatin.
ü Answer:
(a)
Negatively charged DNA is wrapped around positively charged histone octamer to form
nucleosome.
(b)
• Euchromatin: Loosely packed and
transcriptionally active region of chromatin.
•
Heterochromatin: Densely packed and inactive region of chromatin.
3. Identify the
disadvantages of RNA over DNA as a genetic material and explain it. (2)
ü Answer:
It
is catalytic and hence reactive. It is single stranded and has 2’-OH group in
sugar. So RNA is less stable and mutate faster.
4. (a) In lac
Operon lactose act as inducer molecule. Evaluate the statement and explain it.
(b) Observe the diagram of lac
Operon and identify labelled parts A, B, C and D. (3)
ü Answer:
(a)
The statement is true. Lactose switches on the lac operon system inducing the action
of structural genes.
(b)
A= Repressor mRNA, B= b-galactosidase, C= Permease D= Transacetylase.