1. Kingdom Monera (Bacteria)
- Bacteria are the most abundant microorganisms.
- Hundreds of bacteria are present in a handful of soil.
- They also live in extreme habitats such as hot springs, deserts, snow, and deep oceans. Many are parasites.
- Based on shape, bacteria are of four types: Coccus (spherical), Bacillus (rod-shaped), Vibrio (comma-shaped), and Spirillum (spiral).
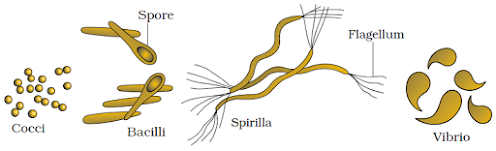
- Some bacteria are autotrophic (synthesize food from inorganic substrates). The majority are heterotrophs (depend on other organisms or dead organic matter for food).
I. Archaebacteria
- They live in the harshest habitats such as extreme salty areas (halophiles), hot springs (thermoacidophiles), and marshy areas (methanogens).
- Archaebacteria have a different cell wall structure for their survival in extreme conditions.
- Methanogens are present in the guts of ruminant animals (cows, buffaloes, etc.). They produce methane (biogas) from the dung of these animals.
II. Eubacteria (‘True Bacteria’)
- They have a rigid cell wall and a flagellum (if motile).
- They include autotrophs (photosynthetic and chemosynthetic) and heterotrophs.
a. Photosynthetic Autotrophs (e.g., Cyanobacteria)
- They have chlorophyll a similar to green plants.
- Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) are unicellular, colonial, or filamentous, marine, or terrestrial algae.
- The colonies are generally surrounded by a gelatinous sheath.
- They often form blooms in polluted water bodies.
- Some of them fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells (heterocysts). E.g., Nostoc and Anabaena.

b. Chemosynthetic Autotrophs
- They oxidize inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia and use the released energy for ATP production.
- They help in recycling nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, iron, and sulfur.
c. Heterotrophic Bacteria
- They are the most abundant in nature.
- The majority are important decomposers.
Impacts of Heterotrophic Bacteria on Human Affairs:
- They are used to make curd from milk.
- Production of antibiotics.
- Fixing nitrogen in legume roots, etc.
- Some are pathogens causing diseases, e.g., cholera, typhoid, tetanus, and citrus canker.
Reproduction in Bacteria
- Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission.
- Under unfavorable conditions, they produce spores.
- They also reproduce by a sort of sexual reproduction (DNA transfer from one bacterium to another).

- Mycoplasmas are organisms without a cell wall. They are the smallest living cells. They can survive without oxygen. Many are pathogenic in animals and plants.
